
CognitiveLab Team
Share this post
The Multilingual Document Challenge
A pharmaceutical manufacturer's quality team spends 30% of their time just maintaining consistency between language versions of the same document across facilities in Poland, Portugal, and Germany. A construction project manager in Singapore needs critical safety specifications from a Korean supplier's documentation, but language barriers delay risk identification. A customer support agent in Brazil searches their knowledge base for a solution-only to find the answer exists in English documentation they can't effectively access.
These aren't edge cases. They represent the daily reality facing global enterprises, researchers, and organizations operating across linguistic boundaries. While AI has made tremendous strides in understanding English documents, 76% of online shoppers prefer information in their native language, and 40% will never buy from websites in other languages. For businesses with global operations, multilingual documentation isn't a nice-to-have-it's mission-critical.
The technical reality is even more challenging. When master documents require updates, synchronizing changes across multiple language versions creates a documentation management nightmare. Documentation delays from multilingual review cycles slow batch releases and impact market availability. For construction projects overseas, the inability to quickly search and retrieve information from foreign-language documents increases project risk and costs.
The numbers tell a stark story: existing state-of-the-art document retrieval systems score just 0.284 on cross-lingual retrieval tasks-performance so poor it's essentially unusable in production. In our testing, these systems consistently fail to find relevant documents when queries and documents are in different languages, making them unreliable for real-world multilingual workflows. When your business operates in multiple languages, this gap translates directly into lost productivity, missed opportunities, and frustrated teams.
Introducing NetraEmbed: Breaking the Language Barrier
Today, we're excited to announce NetraEmbed and ColNetraEmbed, two models that fundamentally change what's possible in multilingual and multimodal document retrieval. These aren't incremental improvements-they represent a 152% leap forward in performance, bringing cross-lingual document search from barely functional to genuinely useful.
What makes this particularly powerful is the multimodal approach. Traditional document search systems rely on extracting text through OCR, which loses critical information like charts, diagrams, tables, and document layout. NetraEmbed processes documents as images, preserving all visual elements and understanding how information is structured on the page. This means you can search for "revenue growth chart" and find the actual chart, or search for "organizational hierarchy" and locate the relevant diagram-across any of the 22 supported languages.
The Numbers That Matter
NetraEmbed achieves a score of 0.716 NDCG@5 on cross-lingual retrieval, compared to the previous best of 0.284. In practical terms, this means the system can now reliably find the right document even when your query and documents are in different languages. For monolingual searches, the performance is even better at 0.738 NDCG@5, an 80% improvement over existing solutions.
Here's what makes this particularly compelling for businesses: we didn't sacrifice English performance to achieve multilingual capability. NetraEmbed scores 0.554 on standard English benchmarks, remaining competitive with models designed exclusively for English. You get global capability without compromising on your primary language.
The system supports 22 languages spanning diverse writing systems: English, Spanish, French, German, Italian, Hindi, Marathi, Sanskrit, Kannada, Telugu, Tamil, Malayalam, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Bengali, Gujarati, Odia, Punjabi, Russian, and Thai. Whether you're working with Latin script, Devanagari, Chinese characters, Arabic script, or any combination thereof, NetraEmbed handles them with consistent reliability.
Two Models, Different Strengths
We're releasing two variants to serve different deployment needs:
NetraEmbed is our flagship single-vector model designed for large-scale deployments. It stores each document as a compact embedding-just 10 KB compared to 2.5 MB for traditional multi-vector approaches. This 250x efficiency gain means you can index millions of documents without breaking the bank on storage costs. For enterprises managing vast document repositories, this efficiency isn't just convenient-it's transformative.
The model offers flexible sizing through Matryoshka representation learning. Choose 768 dimensions for maximum speed and minimal storage (retaining 95% of full accuracy), 1536 dimensions for balanced performance, or the full 2560 dimensions for absolute maximum accuracy. The beauty of this approach? You can switch between these sizes without retraining or reloading the model.
ColNetraEmbed takes a different approach with multi-vector representations, offering token-level matching for applications requiring fine-grained retrieval. It scores 0.637 on cross-lingual tasks and 0.670 on monolingual searches. While slightly less accurate than NetraEmbed, it provides superior interpretability-you can see exactly which parts of a document matched your query, making it ideal for compliance and legal applications where explainability matters.
Try It Yourself
Experience NetraEmbed in action with our interactive demo. Upload your documents in any of the 22 supported languages and search across them-even with queries in a different language. The system understands both text and visual elements like charts and tables.
Why Multimodal Matters
The multimodal capability isn't just a technical feature-it's a fundamental advantage for real-world document search:
Visual Information Preservation: Financial reports aren't just text-they're charts showing trends, tables comparing metrics, and diagrams illustrating relationships. OCR-based systems extract the text but lose the visual context. NetraEmbed sees the whole picture, literally. When you search for "quarterly revenue comparison," it can find the bar chart showing Q1 vs Q2 vs Q3, even if that information isn't explicitly written in text.
Layout Understanding: The way information is arranged on a page often conveys meaning. A two-column contract has different sections serving different purposes. A research paper's structure-abstract, methodology, results-carries semantic value. NetraEmbed understands these structural patterns, improving retrieval accuracy for documents where layout matters.
Cost-Effective at Scale: Running accurate OCR pipelines at scale can be expensive, especially for multilingual documents requiring language-specific processing. With modern vision-language models excelling at Document Visual Question Answering (DocVQA), there's a more efficient approach: embed document images directly with NetraEmbed for retrieval, then pass only the relevant retrieved documents to VLMs for question answering. This two-stage pipeline dramatically reduces costs-you only pay for expensive VLM inference on the handful of documents that matter, rather than processing your entire corpus through OCR and then VLMs. At enterprise scale with millions of documents, this architecture can reduce processing costs by orders of magnitude while maintaining high accuracy.
No OCR Errors: Every additional processing step introduces errors. Poor scan quality, unusual fonts, mixed languages, or handwritten annotations can break OCR systems. By processing documents as images, NetraEmbed sidesteps these failure modes entirely. It works equally well with pristine PDFs and low-quality scans.
Complex Documents: Try searching for information in a document mixing Hindi text with English technical terms, containing embedded charts, and using domain-specific symbols. Traditional systems struggle with even one of these challenges. NetraEmbed handles all of them simultaneously because it processes the complete visual and textual context together.
Real-World Applications
For multinational corporations, NetraEmbed means your knowledge management system finally works across all your offices. That product specification in German? Instantly findable by your team in India. Those compliance documents in Japanese? Accessible to your European auditors without translation delays.
Research institutions can now build truly global academic search systems. A researcher querying in English can discover relevant papers published in Chinese or Arabic, dramatically expanding the accessible knowledge base and accelerating scientific collaboration across linguistic boundaries.
Cultural heritage organizations can make their multilingual archives genuinely searchable. Historical documents in various regional languages become accessible to scholars worldwide, democratizing access to cultural knowledge that was previously locked behind language barriers.
Introducing NayanaIR Benchmark: A New Standard for Multilingual Document Retrieval
A critical challenge in advancing multilingual document retrieval has been the absence of comprehensive evaluation frameworks. Existing benchmarks primarily focus on English or limited language coverage, making it impossible to rigorously evaluate systems across diverse writing systems and linguistic families. To address this gap, we're introducing NayanaIR Benchmark - comprehensive multilingual multimodal document retrieval benchmark.
Why NayanaIR Matters:
The benchmark provides 23 datasets covering both cross-lingual retrieval (queries in one language, documents in another) and monolingual retrieval across all 22 supported languages. With nearly 28,000 document images and over 5,400 queries in BEIR-compatible format, it enables standardized evaluation across diverse script families including Latin, Devanagari, Dravidian, CJK, Arabic, and more.
What makes NayanaIR particularly valuable is its comprehensive coverage and balanced design. Each monolingual dataset contains approximately 1,000 documents and 200 queries, while the cross-lingual dataset spans all 22 languages with 5,870 parallel documents. This balanced structure ensures fair comparison across languages and prevents bias toward high-resource languages. The benchmark uses industry-standard metrics (NDCG@5/10, Recall@5/10, MAP@10, MRR@10) and graded relevance scoring, making results directly comparable with existing English benchmarks.
For the research community, NayanaIR provides the foundation to develop and evaluate truly multilingual document retrieval systems. It removes the barrier of having to create language-specific evaluation datasets and enables researchers to measure progress across the full spectrum of linguistic diversity. Whether you're building commercial systems or advancing academic research, NayanaIR offers the rigorous evaluation framework needed to push the field forward.
The Technology Behind the Breakthrough
Our M3DR (Multilingual Multimodal Document Retrieval) framework powers both NetraEmbed and ColNetraEmbed. We developed a sophisticated synthetic data generation pipeline that creates parallel multilingual document datasets while preserving layout and visual elements-critical for documents where structure conveys meaning.
The training process uses advanced query synthesis with large vision-language models, generating diverse question types across all 22 languages. This ensures the models don't just memorize patterns but truly understand the relationship between queries and document content across linguistic boundaries.
NetraEmbed is part of our broader Nayana initiative-a comprehensive effort to build multilingual, multimodal document intelligence that goes beyond retrieval to deep understanding. While NetraEmbed finds documents, our upcoming Nayana models will answer questions about them, extract insights, and enable true document comprehension across languages.
Getting Started
Ready to integrate NetraEmbed into your systems? Here's how the complete ingestion and retrieval workflow works:
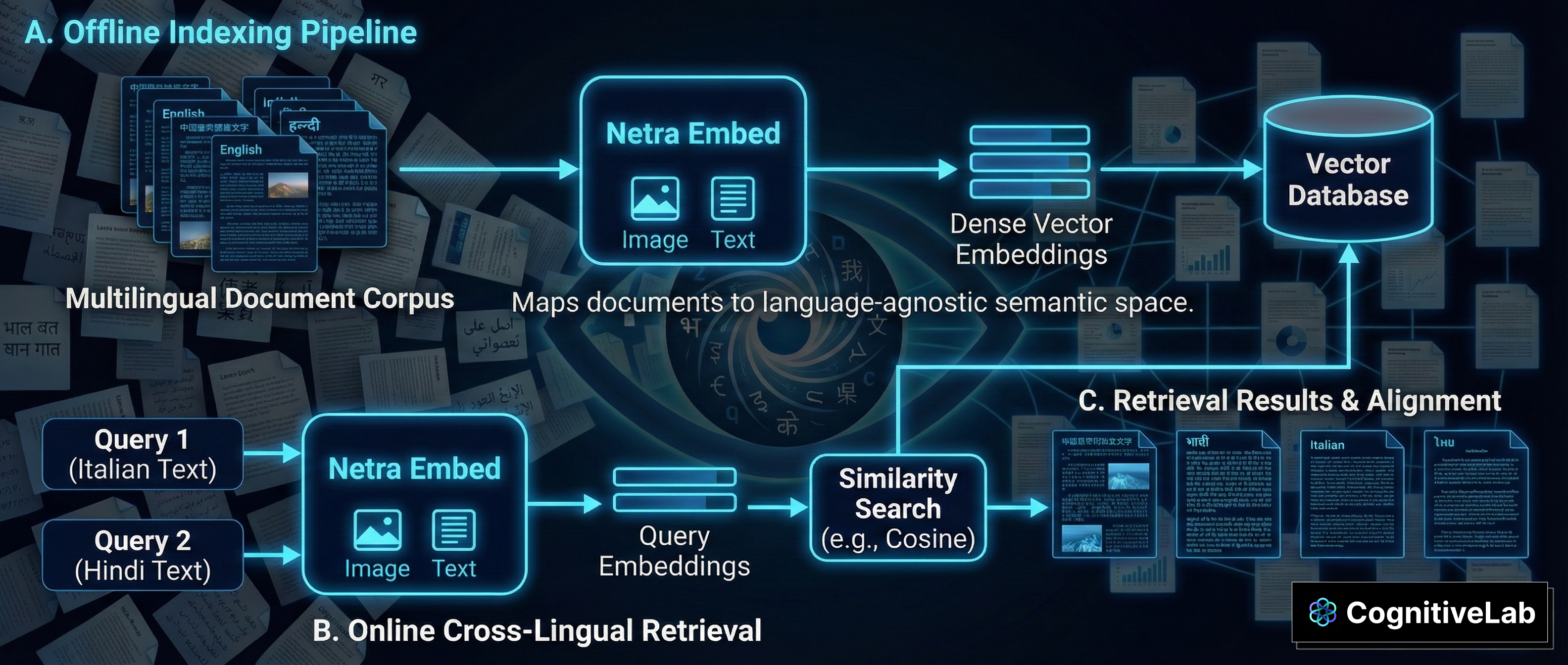 Figure: End-to-end workflow showing document ingestion, embedding generation, and multilingual retrieval with NetraEmbed
Figure: End-to-end workflow showing document ingestion, embedding generation, and multilingual retrieval with NetraEmbed
How It Works
Document Ingestion: Your multilingual documents (PDFs, images, scans) are processed as images, preserving all visual elements including charts, tables, and layout. NetraEmbed generates compact embeddings (10 KB per document) that capture both textual and visual information. These embeddings are stored in your vector database of choice (Pinecone, Weaviate, Qdrant, etc.).
Query Processing: When a user submits a search query in any of the 22 supported languages, the query text is similarly embedded using NetraEmbed. The model understands the semantic intent across languages, enabling true cross-lingual retrieval.
Retrieval: The system performs similarity search in your vector database to find the most relevant documents, regardless of the language mismatch between query and documents. Results are ranked by relevance, and you can retrieve documents in Japanese using an English query, or vice versa-all with state-of-the-art accuracy.
Integration with VLMs: For question-answering workflows, pass the retrieved document images directly to vision-language models for DocVQA. This eliminates OCR overhead and cost, as you only run expensive VLM inference on the handful of relevant documents identified by NetraEmbed.
Resources
Both models are available on HuggingFace with complete documentation and implementation guides. The NetraEmbed model and ColNetraEmbed model include example code for common use cases, from simple document search to complex RAG pipelines.
The NayanaIR Benchmark is also freely available for researchers and teams who want to evaluate performance on their specific language combinations or compare against their own systems.
Our research paper, "M3DR: Towards Universal Multilingual Multimodal Document Retrieval", details the complete methodology and is available on arXiv. The paper includes extensive ablation studies, architectural decisions, and performance analyses across all language pairs.
Performance at a Glance
Cross-Lingual Retrieval Performance
Here's how NetraEmbed compares to existing solutions on cross-lingual retrieval (when query and document are in different languages):
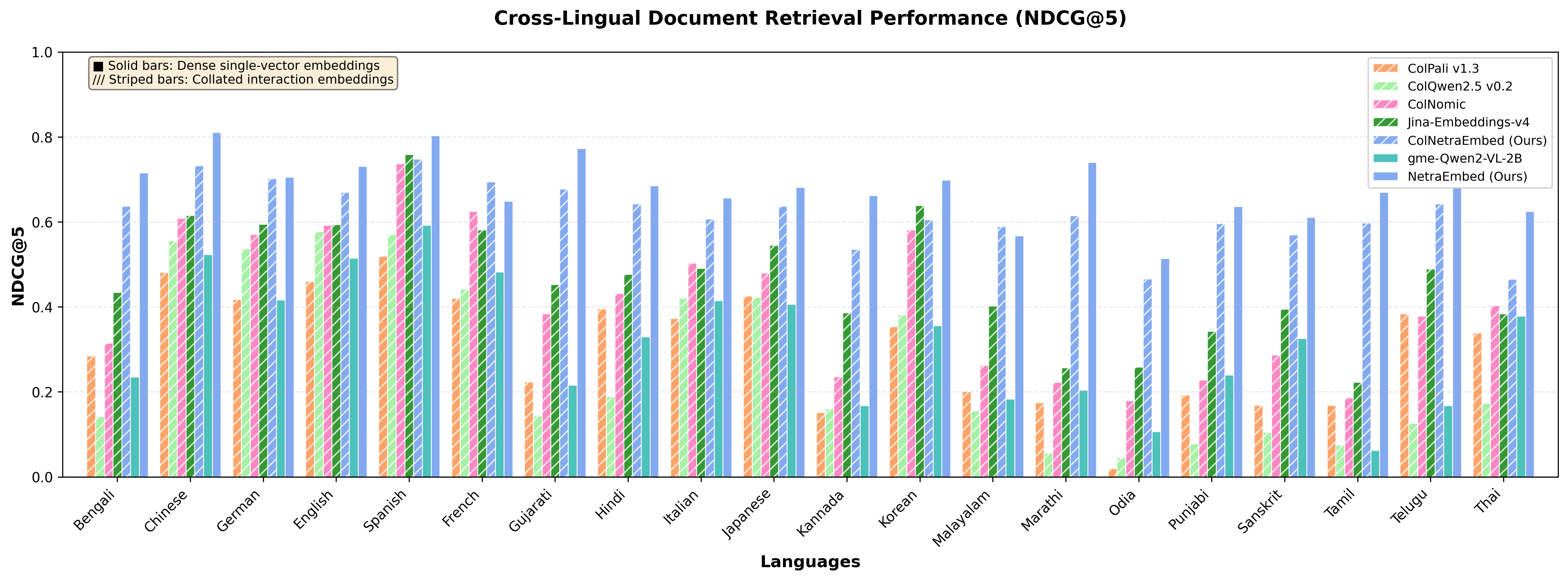 Figure: Cross-lingual retrieval performance comparison showing NetraEmbed's 152% improvement over existing baselines
Figure: Cross-lingual retrieval performance comparison showing NetraEmbed's 152% improvement over existing baselines
| Model | NDCG@5 | Recall@10 | MAP@10 | MRR@10 | Improvement over ColPali |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NetraEmbed (Ours) | 0.716 | 0.871 | 0.703 | 0.775 | +152% |
| ColNetraEmbed (Ours) | 0.637 | 0.700 | 0.610 | 0.610 | +124% |
| Jina-Embeddings-v4 | 0.435 | 0.435 | 0.390 | 0.548 | +53% |
| ColNomic-Embed-3B | 0.315 | 0.320 | 0.267 | 0.444 | +11% |
| ColPali-v1.3 | 0.284 | 0.347 | 0.249 | 0.403 | Baseline |
| ColQwen2.5-v0.2 | 0.143 | 0.160 | 0.127 | 0.220 | -50% |
| GME-Qwen2-VL-2B | 0.235 | 0.308 | 0.209 | 0.314 | -17% |
Monolingual Retrieval Performance
For searches within a single language, NetraEmbed maintains exceptional consistency:
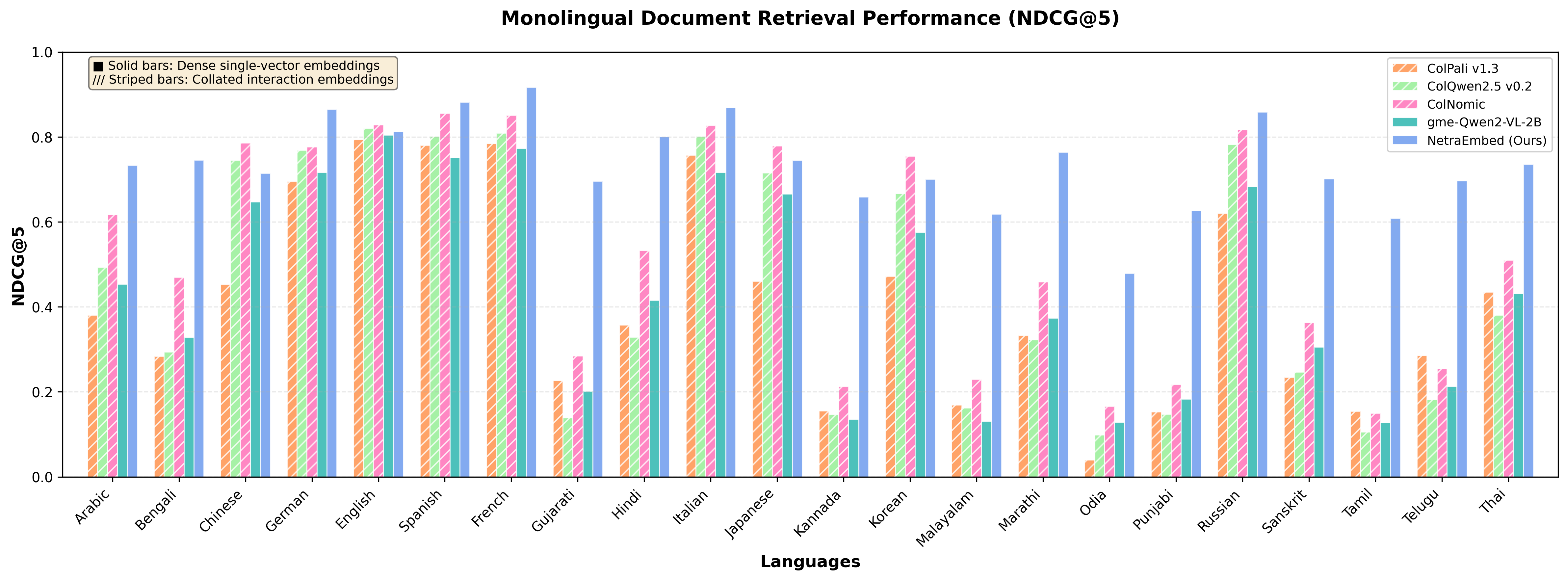 Figure: Monolingual retrieval performance showing consistent state-of-the-art results across all supported languages
Figure: Monolingual retrieval performance showing consistent state-of-the-art results across all supported languages
| Model | NDCG@5 | Recall@10 | MAP@10 | MRR@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NetraEmbed (Ours) | 0.738 | 0.844 | 0.709 | 0.751 |
| ColNetraEmbed (Ours) | 0.670 | 0.764 | 0.645 | 0.686 |
| ColNomic-Embed-3B | 0.534 | 0.603 | 0.515 | 0.546 |
| GME-Qwen2-VL-2B | 0.444 | 0.525 | 0.426 | 0.452 |
| ColQwen2.5-v0.2 | 0.453 | 0.513 | 0.437 | 0.464 |
| ColPali-v1.3 | 0.410 | 0.484 | 0.393 | 0.422 |
English Performance (ViDoRe v2 Benchmark)
NetraEmbed maintains competitive English performance while excelling at multilingual tasks:
| Model | NDCG@5 | Recall@10 | MAP@10 | MRR@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ColQwen2.5-v0.2 | 0.592 | 0.664 | 0.484 | 0.711 |
| Jina-Embeddings-v4 | 0.576 | 0.686 | - | - |
| GME-Qwen2-VL-2B | 0.574 | 0.630 | 0.466 | 0.690 |
| ColNomic-Embed-3B | 0.556 | 0.633 | 0.451 | 0.672 |
| NetraEmbed (Ours) | 0.554 | 0.637 | 0.437 | 0.647 |
| ColNetraEmbed (Ours) | 0.551 | 0.664 | 0.445 | 0.645 |
| ColQwen2-v1.0 | 0.545 | 0.640 | 0.438 | 0.653 |
| ColPali-v1.3 | 0.538 | 0.627 | 0.436 | 0.644 |
Matryoshka Embedding Flexibility
NetraEmbed offers flexible dimension sizes for different deployment scenarios:
| Dimensions | Storage/Doc | NDCG@5 | Relative Performance | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 768 | ~3 KB | 0.680 | 95.0% | Billion-scale deployments, edge devices |
| 1536 | ~6 KB | 0.706 | 98.6% | Balanced production systems |
| 2560 (full) | ~10 KB | 0.716 | 100.0% | Maximum accuracy requirements |
Key Insight: The 768-dimensional variant retains 95% of full performance while reducing storage by 70%, making large-scale deployment economically viable.
What's Next: From Retrieval to Understanding
NetraEmbed solves the critical first step-finding the right documents across languages. But this is just the beginning of our vision for multilingual document intelligence.
As part of our Nayana initiative, we're developing specialized vision-language models that don't just retrieve documents-they understand and answer questions about them. Imagine uploading a financial report in Japanese and asking detailed questions in English: "What was the revenue growth in Q3?" or "Which product line had the highest margin?" These models will process the document image directly and provide accurate answers, preserving all visual context from charts and tables.
The Nayana family of models represents the next frontier in multilingual, multimodal document intelligence. Where NetraEmbed finds the right document, Nayana models will extract insights from it-across any of the 22 supported languages, understanding both text and visual elements like charts, diagrams, and complex layouts. This creates a complete pipeline: retrieve with NetraEmbed, then understand with Nayana.
We're also expanding language coverage beyond the current 22, with particular focus on truly low-resource languages where the need is greatest. Additionally, we're developing specialized fine-tuned variants for specific industries-legal document search, medical records retrieval, and academic research applications. Each domain has unique requirements, and we're building solutions that address them while maintaining the multilingual capabilities that make our models unique.
For enterprises interested in early access to Nayana models, custom deployments, or specialized language support, we offer consultation and collaboration opportunities. Reach out to our team at contact@cognitivelab.in to discuss your specific requirements.
Join the Community
NetraEmbed is built on open research principles. We're releasing our models, the NayanaIR Benchmark, and training methodology to enable the research community to build on this foundation. If you're working on multilingual AI, document understanding, or related challenges, we'd love to collaborate.
Explore the models on HuggingFace, read the research paper, and reach out if you have questions or feedback at contact@cognitivelab.in. Together, we can make document intelligence truly universal.
Acknowledgments
This work benefited from compute credits for training, inference, and evaluation provided by Modal, acknowledged as a compute sponsor. Dataset curation and synthesis were supported by the Meta Llama Impact Grant through our Nayana initiative. We appreciate Meta for continued support of our research efforts at CognitiveLab.
Quick Links:
- NetraEmbed Model on HuggingFace - Download and integrate the single-vector model
- ColNetraEmbed Model on HuggingFace - Multi-vector variant for fine-grained retrieval
- NayanaIR Benchmark - Evaluation datasets across 22 languages
- Nayana Initiative - Next-generation document understanding models
- Research Paper on arXiv - M3DR: Towards Universal Multilingual Multimodal Document Retrieval
- CognitiveLab - Explore our other AI research and products
- Contact Us - Questions, collaborations, or enterprise inquiries